Cell and Molecular Terminology
Dictionary
Microscopes Techniques
- EM microscopy- Is the use of an electron microscope that are used study ultra structure inorganic specimens such as: microorganism, cells, biopsy, metals, and large molecules. The microscope uses a beam of electrons as light. The wavelength that it produced it's about 100,000 times smallest than a light microscopes.
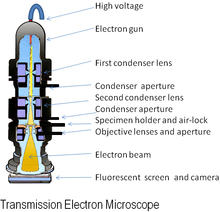
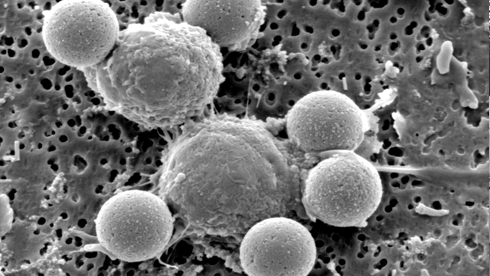
- Light microscope- Also known as the optical microscope, this type of microscope uses visible light and lenses to visualize images of the samples. The optical microscope has being the initial invention to bring out some other microscope that as well uses light. For example: fluorescence microscopy, dark and bright field, digital microscope.

- Force Spectrum microscopy- It's the application technique of Brownian motion, which is the motion of particles that are suspended in fluid. This can amplify the magnitude of random forces that can interfered with the oscillation frequency of particles when is viewed from a spectrum microscope.

- Polarizing microscope- Another name for the polarizing microscope is petrographic microscope and mainly used for geological specimens, although this microscope has being a great used in medicine and biology. The main component that differentiates from other microscopes is that uses polarized light, which are light waves traveling in one direction.






No comments:
Post a Comment